Modifications de génomes, obtention de nouveaux organismes

Genetic modifications Mutants, GMO and the others
Cette séance s’inscrit après l’étude de la notion de gène ayant un locus sur un chromosome et responsable de caractère hérité et donc transmissible. Pendant l’étude des gènes, la notion de maladie héréditaire est apparue avec de la part des élèves des interrogations sur les causes et les thérapies.
Les objectifs de cette séance sont donc
– les modifications du génome (mutations et transgénèse)
– la collecte d’informations et la communication
Le déroulement proposé se découpe en deux parties
– une partie qui étudie les différentes façons de modifier les génomes et y associe des activités d’évaluation de la compréhension de ces mécanismes
– une partie plus "au choix" et autonome sur la thérapie génique
**I. Different ways or means to change genetic traits or the techniques dealing with living organisms : biotechnology
Study of a text extracted from a web site “Union of concerned scientists” on Biotechnologies
http://www.ucsusa.org/food_and_envi...
***Consignes :
— Read the first paragraph (one student loud), what is the topic ?
we complete the title biotechnology
Second paragraph Traditional biotechnologies :
each student reads the paragraph in order to find means to change a genetic trait,
***Consignes :
Use two colours to circle the two method and underline the name of the two methods
Report one of the technique : selective breeding : we already know it : it is sexual reproduction and selection of the fittest for the new sexual reproduction application with corn or maize
au videoprojecteur connecté à Internet on peut faire travailler un élève avec la collaboration des autres sur l’animation interactive :
http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/harvest/eng...

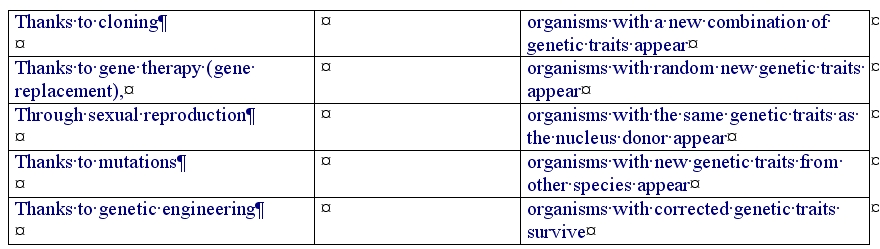
***on aboutit donc à :
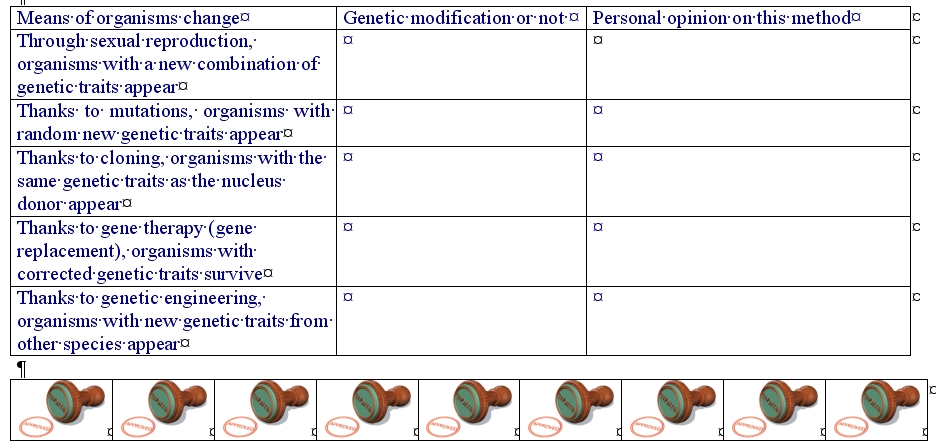
Through sexual reproduction, organisms with a new combination of genetic traits appear
Grâce à la reproduction sexuée sélective, on peut obtenir des organismes avec une nouvelles combinaison de caractéristiques intéressantes et transmissibles aux générations suivantes.
***Consignes :
Report the other technique :
(mutagenesis) : using chemicals or radiation to change genetic material of bacteria for instance.
— What is the name of the process ?
(mutation)
— what is the name of resulting organism ?
(mutant)
— What are the characteristics of the process ?
(random, only a few mutants are desired)
possibilité d’utiliser le site http://learn.genetics.utah.edu/unit...
***on aboutit donc à :
Thanks to mutations, organisms with random new genetic traits appear
Grâce aux mutations, des organismes avec de nouveaux caractères transmissibles peuvent apparaître.
Reading of the third paragraph New biotechnologies
In this paragraph, two techniques are reported, one which changes genetic information and not the other
***Consignes :
circle the two parts of the text in different colours
— Do you know these techniques ?
(yes for cloning, no for gene therapy)
— Does it change genetic information ?
(no for cloning, yes for gene therapy)
— In which cells is the genetic information changed ?
(somatic = non reproductive cell or germ line cells or reproductive cells)
— and what are the consequences ?
(change in the organism only or in the descendants or offspring)
***on aboutit donc à :
Thanks to cloning, organisms with the same genetic traits as the nucleus donor appear
Thanks to gene therapy (gene replacement), organisms with corrected genetic traits survive
Grâce au clonage, on obtient des organismes avec le même génotype que les donneurs de noyaux.
Grâce à la thérapie génique par emplacement de gène, on obtient des des organismes corrigés génétiquement qui peuvent survivre à des maladies mortelles.

Reading of the fourth paragraph Genetic engineering
One student reads aloud the first sentence.
***Consignes :
Which words do you recognize (underline them)
which words are left ?
are they relevant ?
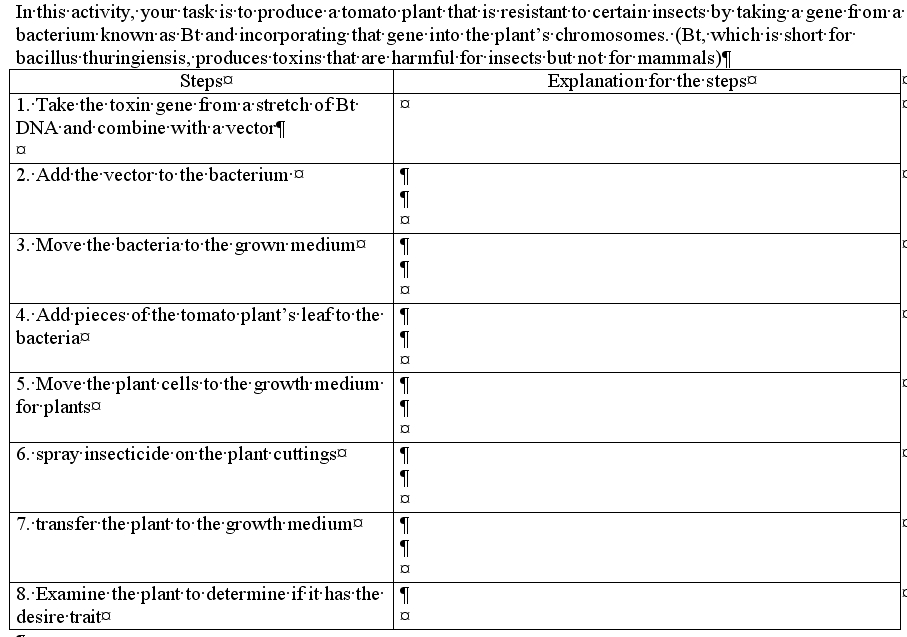
This is a technique which allows organisms from different species to share genes. But the techniques are very sophisticated :
Pour expliquer la technique de transgénèse pour obtenir une PGM, on peut utiliser le site http://www.pbs.org/wgbh/harvest/eng...
Example with a gene from a bacteria to fight a pest (insect eating a plant)

or Oral animation : gene insertion in a bacteria http://www.dnai.org/text/mediashowc...
***on aboutit donc à :
Thanks to genetic engineering, organisms with new genetic traits from other species appear
Grâce au génie génétique, on peut obtenir des organismes avec des caractères génétiques issus d’organismes d’une autre espèce.
Assessment with the matching table
Assessment and further with the approved table
To decide if the method is relevant or not and overall in what cases, we have to get a bit more precise information
**II. Further investigation in gene therapy with stem cells
Transgenic manipulations are not allowed on human sexual cells or human egg cell, but researchers may work on stem cells
To better know these cells, we are going to investigate on them within a web site http://gslc.genetics.utah.edu/units...
you will navigate as you like but the quicker the better to find out answers to basic questions on stem cells
Report the information in a convenient way.